Blog
Opportunities for Optical Character Recognition (OCR) in Insurance
AI-powered optical character recognition (OCR) enables insurers to streamline processes and take better control of their data through intelligent automation and machine learning-driven insights.
Key Points
Optical character recognition (OCR) is a form of machine vision and AI-driven document processing that enables insurance applications to extract and analyze text data from unstructured sources like images and PDF documents, leveraging machine learning for enhanced accuracy. It can then be transformed into a structured format and loaded into downstream systems for processing.
Optical character recognition reduces manual intervention in several key areas of the insurance value chain, including:
- Customer Experience
- New Business and Renewals
- Claims
Insurance industry personnel across various departments like sales, underwriting, and claims face the common problem of extracting the right data from disparate sources and transforming it into a format they can analyze and interpret with backend systems.
This process is known as ETL (extract, transform, and load). Insurers that can maximize their ETL capabilities have a powerful competitive advantage.
Unstructured data sources, like PDFs and images, pose a special problem for insurers.AI-driven OCR solutions with deep learning capabilities significantly reduce the need for manual data extraction, improving efficiency and data accuracy.
These duplicative and paper-based processes are both time-consuming and costly. As a result, insurers are looking to rapid and more cost-effective solutions like optical character recognition (OCR).
A Definition of Optical Character Recognition (OCR) in Insurance
Optical character recognition, also known as text recognition, converts text within unstructured data sources (e.g., a photo of an RFP or a PDF of an in-force policy document) into a machine-readable format.
Often, important information is contained within unstructured data sources, such as scanned paper documents, photos, or books. OCR analyzes the documents using AI-powered natural language processing (NLP) and deep learning algorithms, converting text with images into machine-readable characters for advanced data processing and automated decision-making.
How OCR Works
Optical character recognition uses specialized AI and machine learning algorithms to interpret images of words and transform it into structured, strings of machine-readable text that can be processed, indexed, and retrieved.
To function, OCR applications must leverage existing data sets with thousands of scanned documents and images already interpreted by humans. As the OCR application ingests more documents and images, corrected by humans where necessary, it trains and optimizes its algorithms over time. This is how OCR becomes more accurate over time. This also means OCR applications must perform smaller, manageable tasks with human intervention before intaking large data sets with increased automation.
The principles of feature detection and pattern recognition are important to understand optical character recognition.
- Feature detection enables OCR programs to understand different features that make up characters. For example, when a printed image is scanned, humans can read it on the screen, but the computer only sees it as a series of white and black dots. Feature detection looks at “edges”, “blobs”, “corners”, and “ridges” formed from pixels to make a determination of what the symbol or image represents.
- Pattern recognition examines every line of the image and determines if the sequence of dots matches a letter or number, such as a straight line by itself being an “l” or “1.”
There are two important subfields within AI that are key to understanding optical character recognition:
- Computer Vision (CV): CV trains machine learning models to see and interpret visuals similar to how people see and comprehend them. This enables machines to accurately identify and label objects.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP deals primarily with text and speech-to-text translation data and teaches machines to understand human speech. The best NLP programs can even detect more subtle areas of speech like regional variations, slang, and abbreviations.
Key Benefits of OCR in Insurance
New Business Opportunities
A robust OCR process can convert client documents into structured data in a digestible format that can be analyzed for client cross-selling, up-selling, or new business opportunities.
OCR programs can assist sales and underwriting teams by automatically extracting and transforming key details from RFPs and lengthy policy documents. OCR enables insurance sales professionals to streamline and drive efficiencies by automatically scrubbing RFP emails, multiple PDF documents, plan booklets, and even scanned images of policy documents for key details that can be transformed into a format appropriate for processing.
This data can then be loaded into the insurance company’s sales and underwriting systems, like a quoting and rating engine, creating an initial shell quote in seconds.
Additionally, many insurance companies still maintain vast quantities of historical data in unstructured and paper formats. OCR can be used to sift through and capture relevant data enabling business leaders to identify trends, make predictions about the future, and develop new products in response.
Claims Processing
A quick and painless claims experience is key to maintaining customer loyalty and brand reputation. Insurers must also have accurate data for claims processing as inaccurate information can facilitate fraud or lead to legal challenges and penalties.
OCR-enabled AI insurance claims processing software automates claims validation, using predictive analytics and machine learning to improve speed and accuracy with little to no human intervention. For example, clients can take a picture of the receipt from their dentist or car mechanic and send it to their insurer if they’re entitled to coverage. OCR software can structure the data from the image of the receipt and confirm if the transaction is legitimate, if the client is entitled to coverage, and provide the claim – all without direct human intervention.
In 2016, Lemonade famously set a world record for the fastest-processed insurance claim. Their digital assistant, equipped with OCR technologies, received a claim for a stolen $979 coat, checked the claim against the policy, ran 18 different anti-fraud algorithms, and made the payment – all in under three seconds.
Customer Experience
Optical character recognition uses specialized AI and machine learning algorithms to interpret images of words and transform it into structured, strings of machine-readable text that can be processed, indexed, and retrieved.
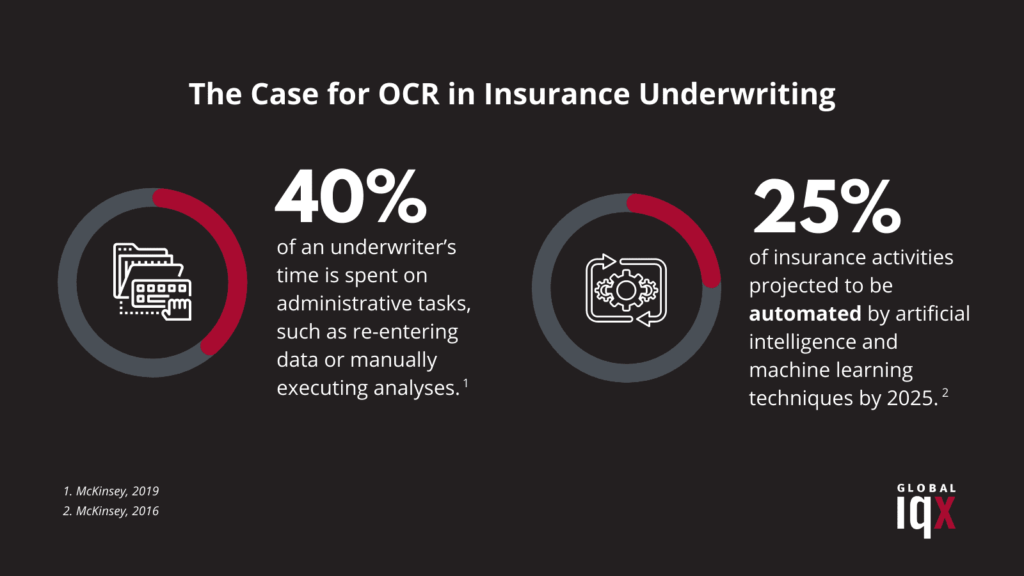
Redundant data entry and lengthy document processing times contribute to a poor downstream customer experience. In fact, 30-40% of an underwriter’s time is spent on administrative tasks, such as re-entering data or manually executing analyses.
Uncontrollable work delays can damage the customer experience as clients demand rapid turnaround times for quotes, enrolment, and claims. In addition, constant delays in claims or policy activation will leave customers feeling stressed and frustrated, worsening the brand image and sales conversions.
OCR technologies can assist insurance companies in replacing manual scanning of data entry and document conversion processes. This can reduce human errors and allow underwriters and other highly skilled workers to focus on more valuable work for their clients. OCR also enables clients to process their own documents, which can help insurers improve the speed of the value chain.
OCR Challenges and Best Practices
While the promise of OCR is clear, like any emerging technology, it has some limitations that must be well-understood by insurers seeking to deploy it.
Insurers should look to solutions that emphasize flexibility and configurability. Effective OCR applications can help insurers extract, transform, and load text data and present it in any fashion they’d like, whether it’s tables, line items, or any other format conducive to business needs.
Image quality is another important consideration when using OCR. Thanks to machine learning, OCR applications are trained to interpret more challenging data sources over time. However, to produce the best results, it is important they are fed a steady stream of high-quality image data with appropriate lighting, contrast, and resolution. Camera applications that contain real-time image quality assessments can be beneficial in helping the user submit documents for clean processing.
OCR, like all AI-based technologies, requires ongoing human inputs and oversight. The more data collected and verified by humans, the faster an OCR application will be trained. Transparency and explainability are always important when dealing with AI, and OCR applications must enable humans to easily understand AI-based outcomes and challenge them.
Insurers need OCR applications that are flexible, straightforward, and customizable but don’t often have the required resources internally. As a result, many insurers are turning to industry partners with access to AI specialists, large data sets for training algorithms, and cost-effective OCR services provided at scale.
OCR: An Increasingly Critical Insurance Technology
Carriers that can accurately extract, transform, and load (ETL) data in real-time can write more business and improve the customer experience.
Optical character recognition (OCR) is a key part of the ETL process. It helps insurance providers convert unstructured data sources containing text (e.g., a scanned document) into a machine-readable, structured format for backend processing.
Insurers can use OCR to assist their customer service teams in transforming the client intake and data entry process. This can help save time, money, reduce errors and improve the overall customer experience.
With 25% of the insurance industry projected to be automated by AI and machine learning techniques by 2025, technologies like OCR are becoming increasingly critical in sectors that need to verify documents accurately in real-time.